



















Grading & Research prides itself on offering the diamond industry a fifth C: Confidence.
We only grade and inscribe diamonds that are 100% natural. Our specially developed industry leading proprietary instruments allow us to be confident that all diamonds we grade are natural and free of treatments as we spearhead the movement of bringing diamond grading into the 21st Century. Our confidence extends further to the consistency and accuracy of our grading throughout all our global laboratories. We believe buyers should have confidence when purchasing a diamond and therefore we strive to offer a level of professionalism and integrity unrivalled in the industry.
About Diamond
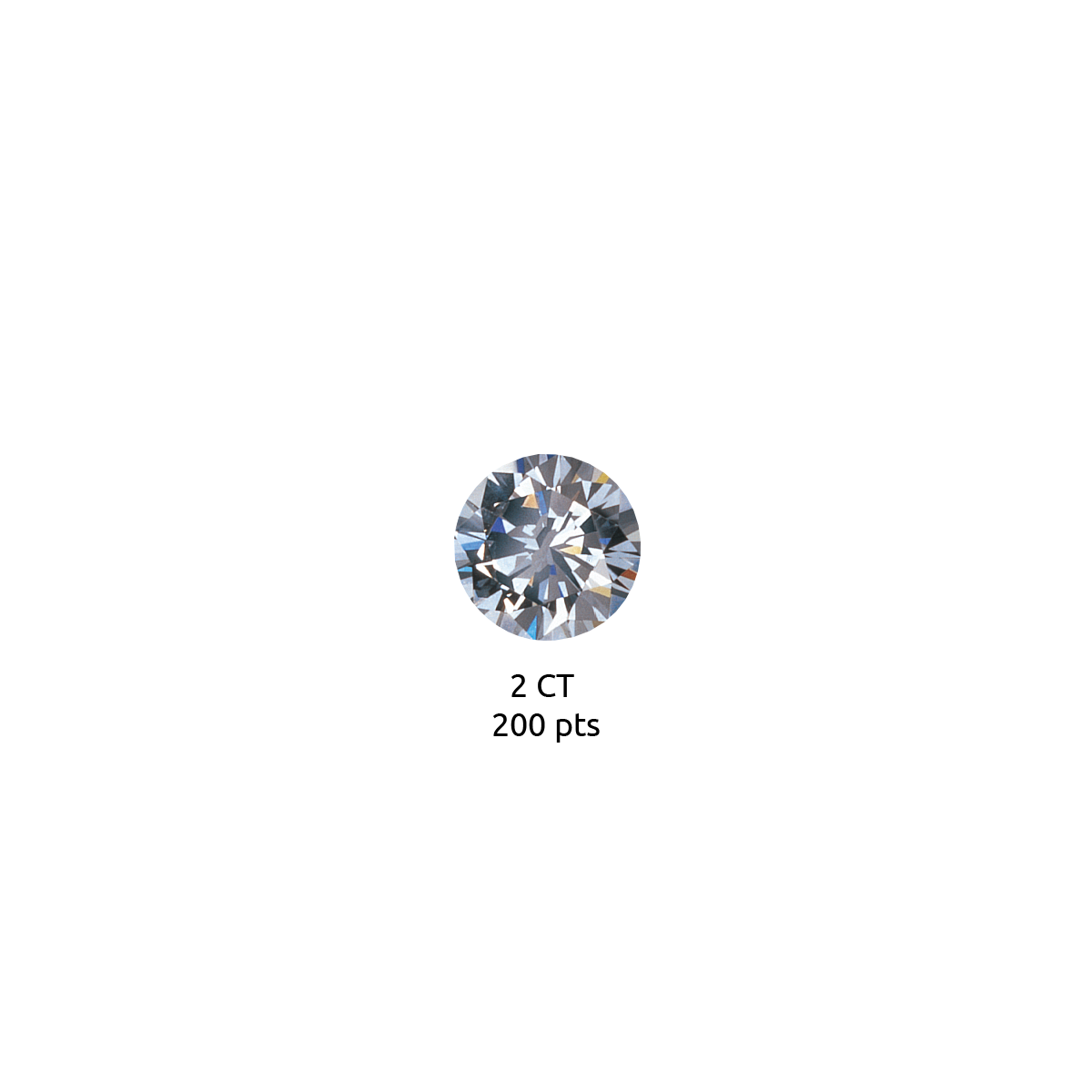
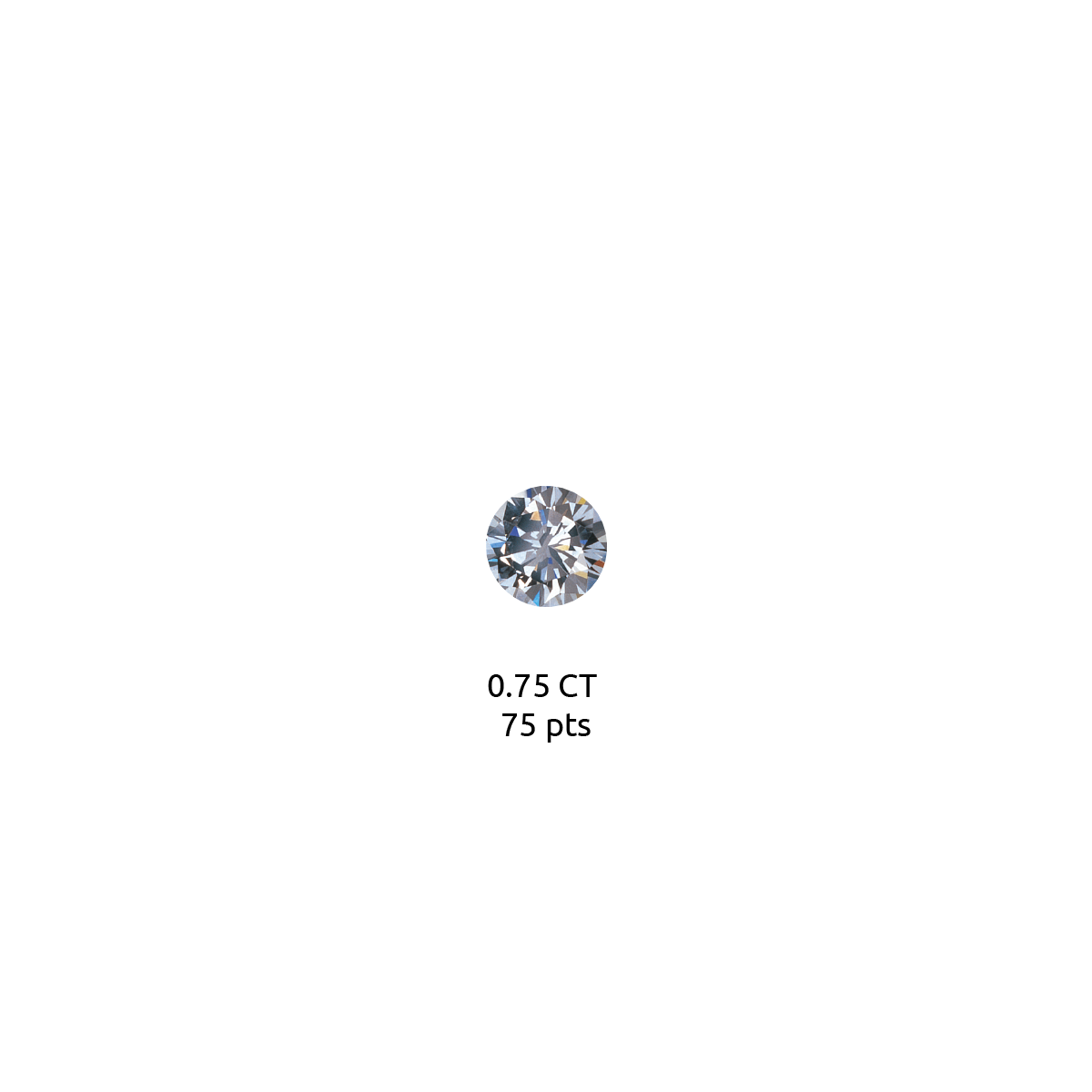
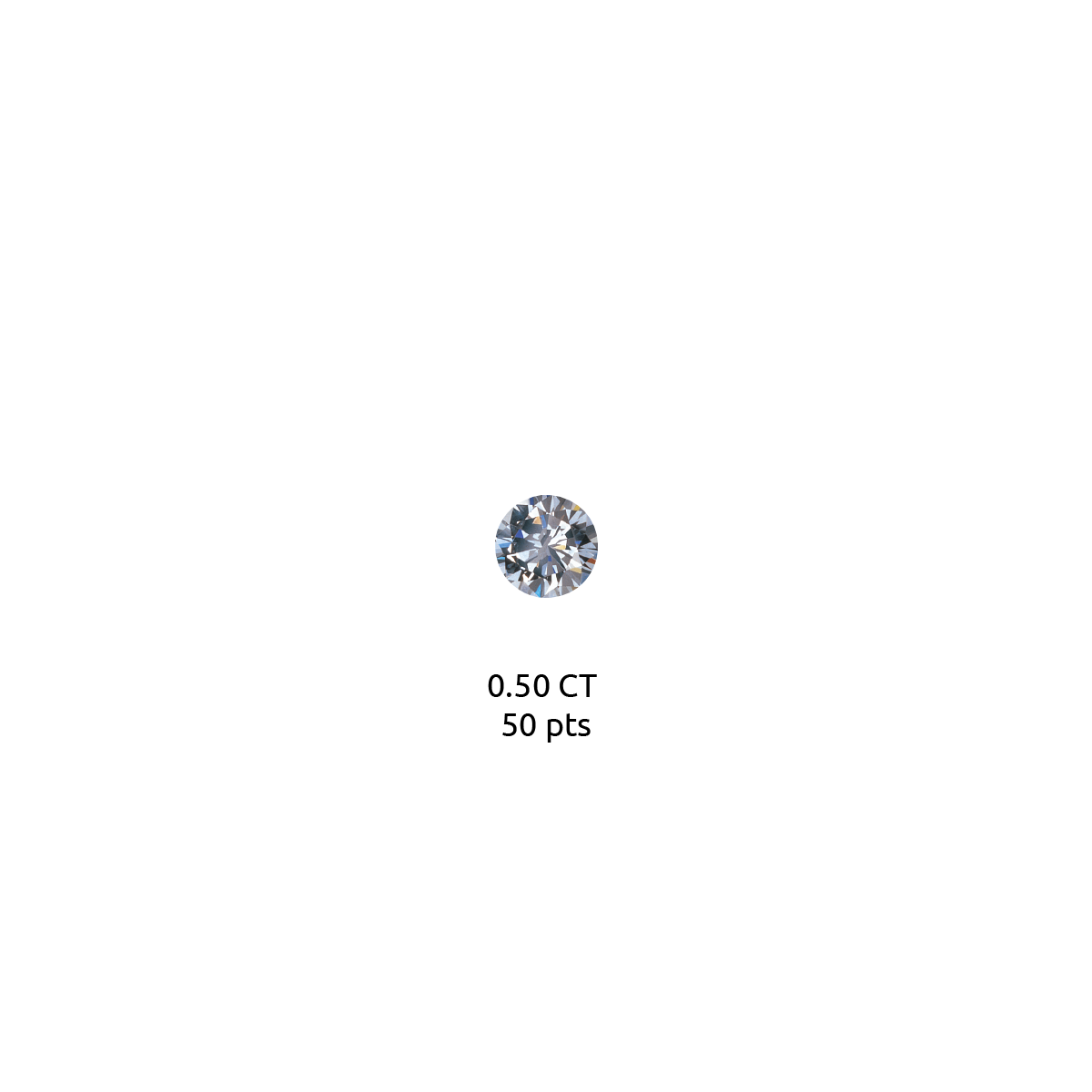
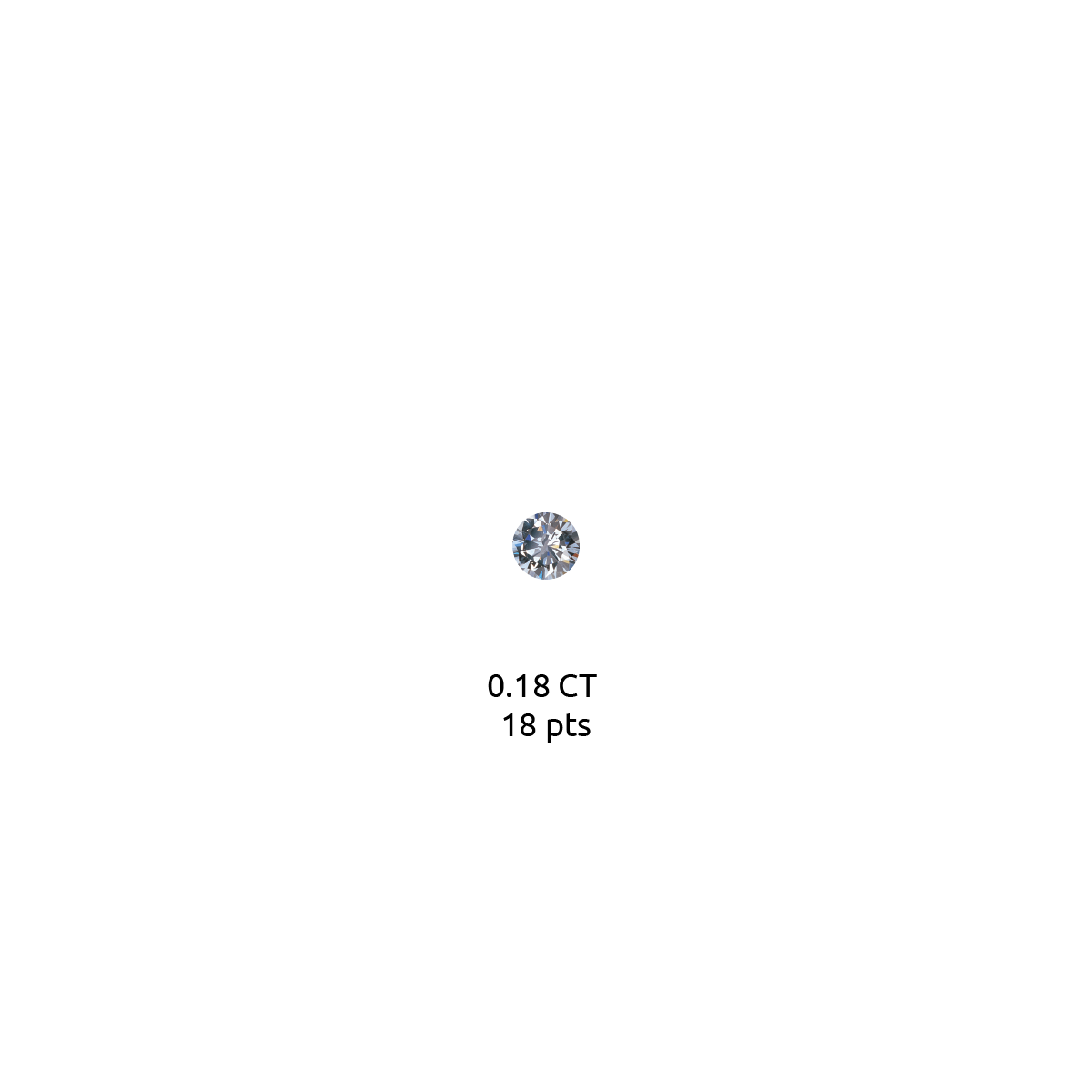
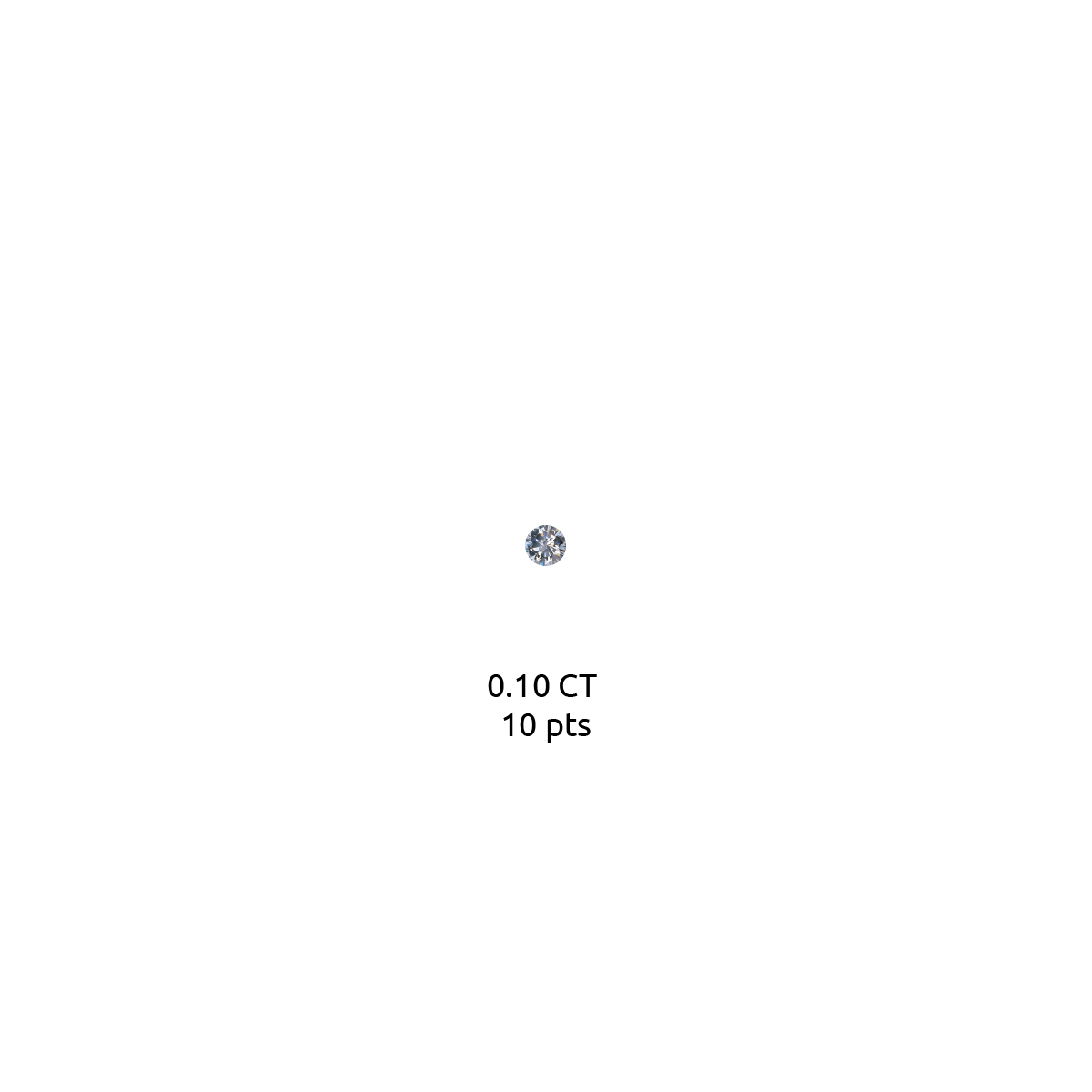
Diamond carat weight is the measurement of how much a diamond weighs. A metric "carat" is defined as 200 milligrams.
Each carat can be subdivided into 100 'points.' This allows very precise measurements to the hundredth decimal place. A jeweler may describe the weight of a diamond below one carat by its 'points' alone. For instance, the jeweler may refer to a diamond that weighs 0.25 carats as a 'twenty-five pointer.' Diamond weights greater than one carat are expressed in carats and decimals. A 1.08 carat stone would be described as 'one point oh eight carats.'


About Diamond
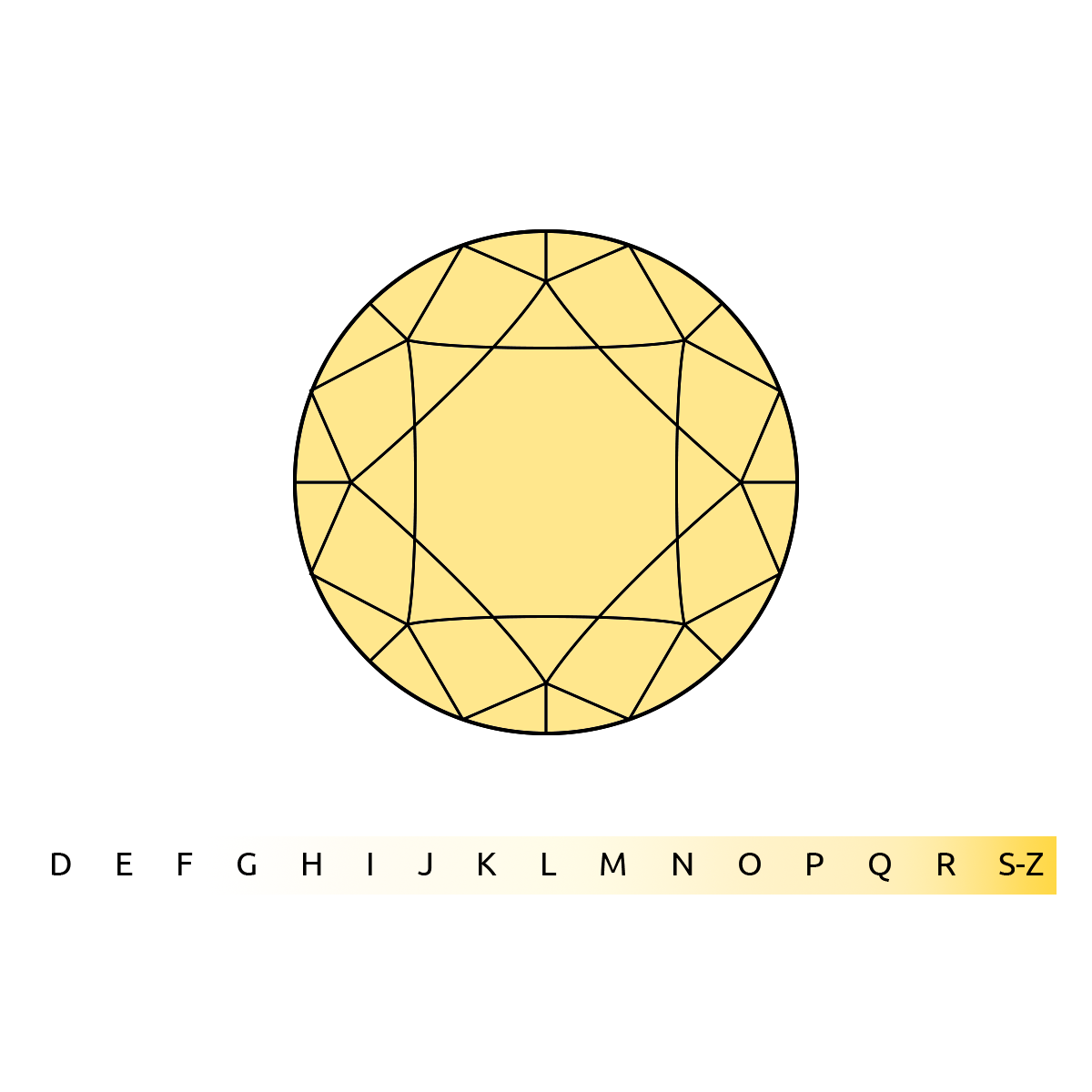
The color evaluation of most gem-quality diamonds is based on the absence of color. A chemically pure and structurally perfect diamond has no hue, like a drop of pure water, and consequently, a higher value. GD's D-to-Z color-grading system measures the degree of colorlessness by comparing a stone under controlled lighting and precise viewing conditions to masterstones of established color value.
GD's D-to-Z color-grading scale is the industry's most widely accepted grading system. The scale begins with the letter D, representing colorless, and continues, with increasing presence of color, to the letter Z.
About Diamond
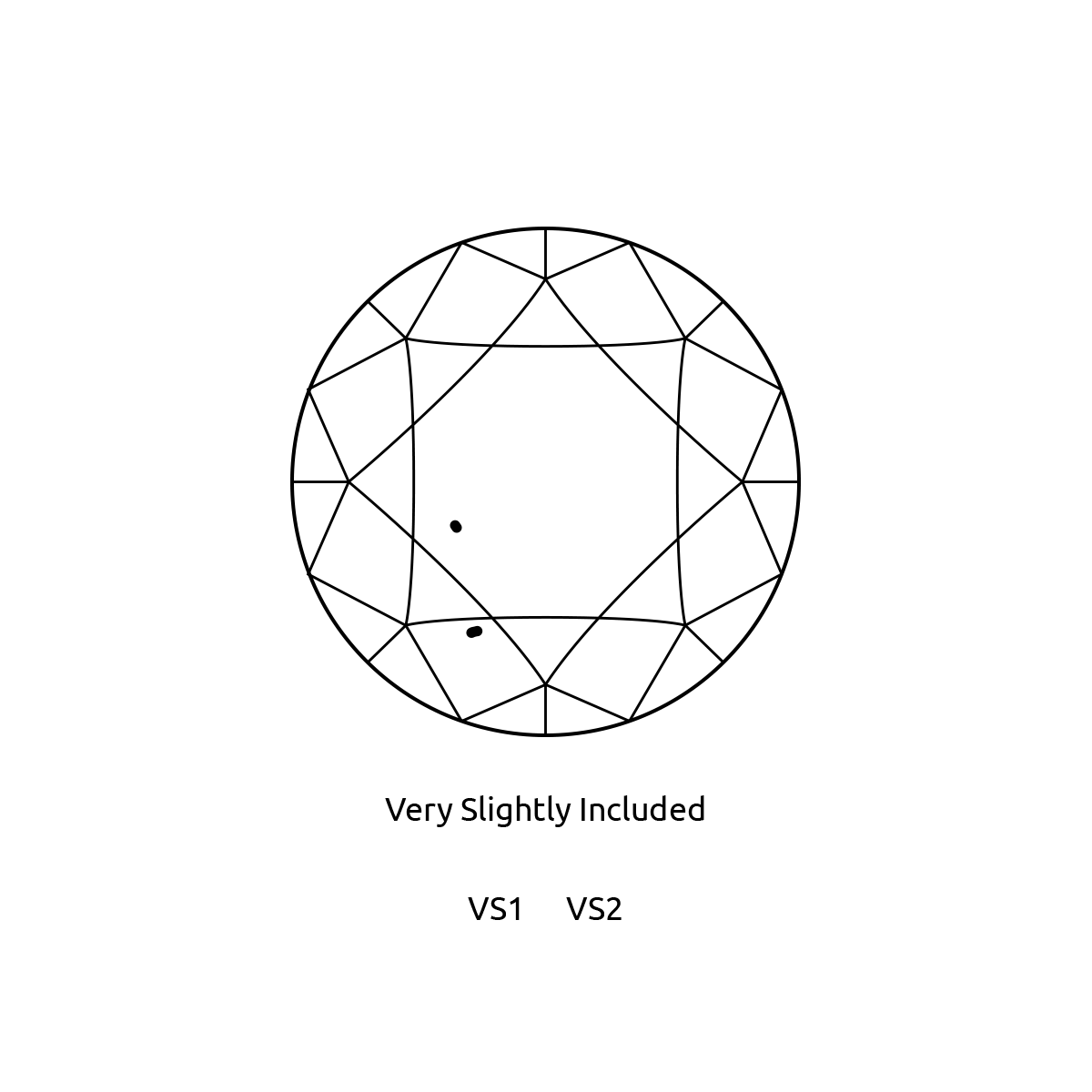
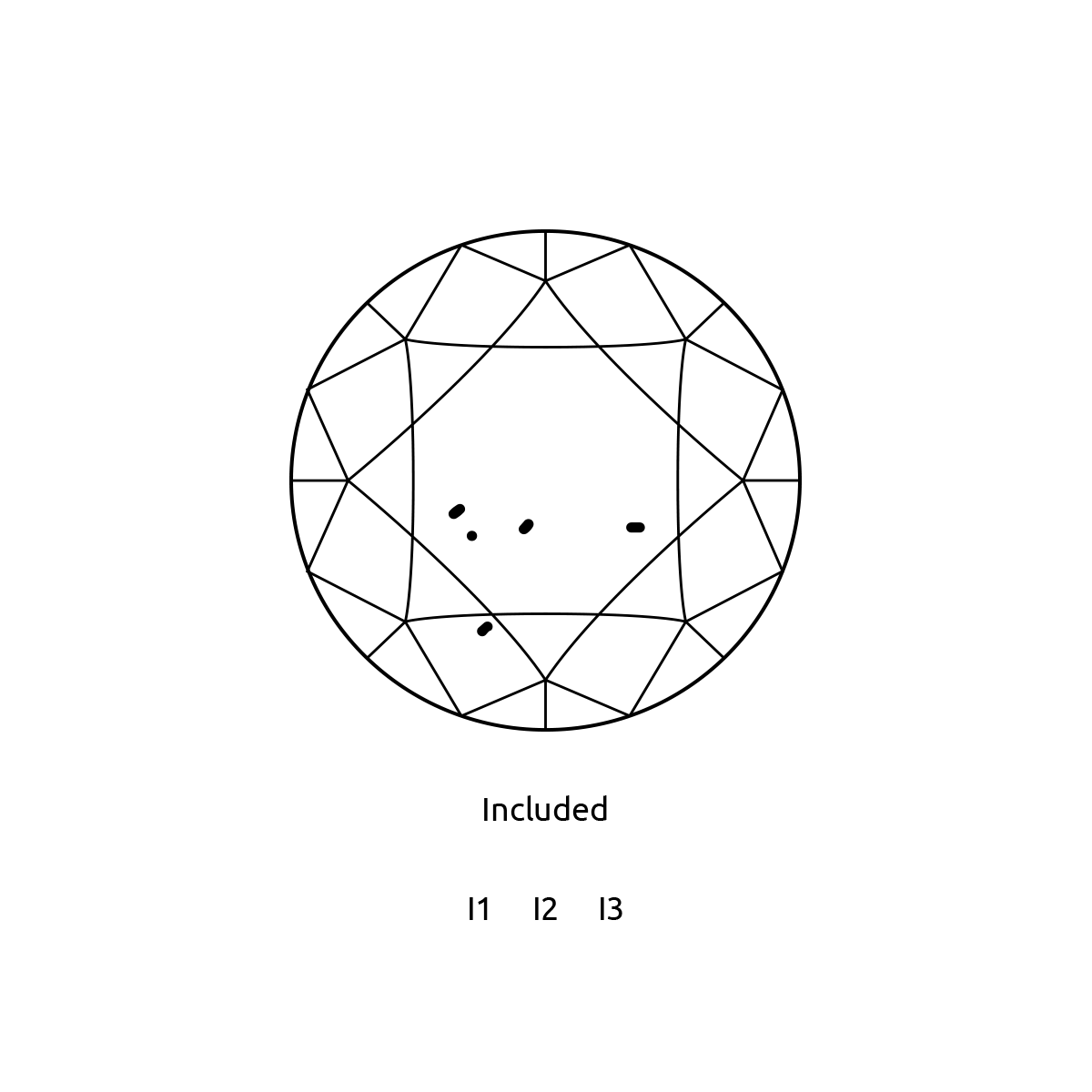
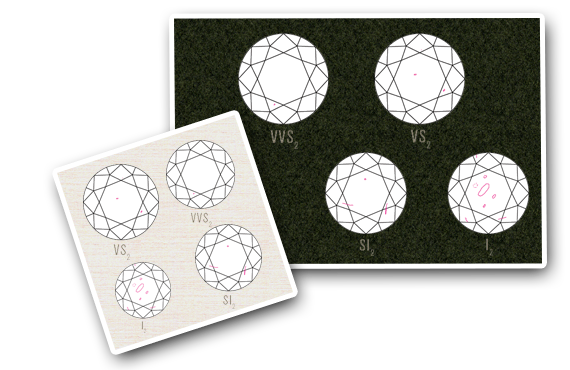
Natural diamonds are the result of carbon exposed to tremendous heat and pressure deep in the earth. This process can result in a variety of internal characteristics called 'inclusions' and external characteristics called 'blemishes.'
Evaluating diamond clarity involves determining the number, size, relief, nature, and position of these characteristics, as well as how these affect the overall appearance of the stone. While no diamond is perfectly pure, the closer it comes, the higher its value.

About Diamond
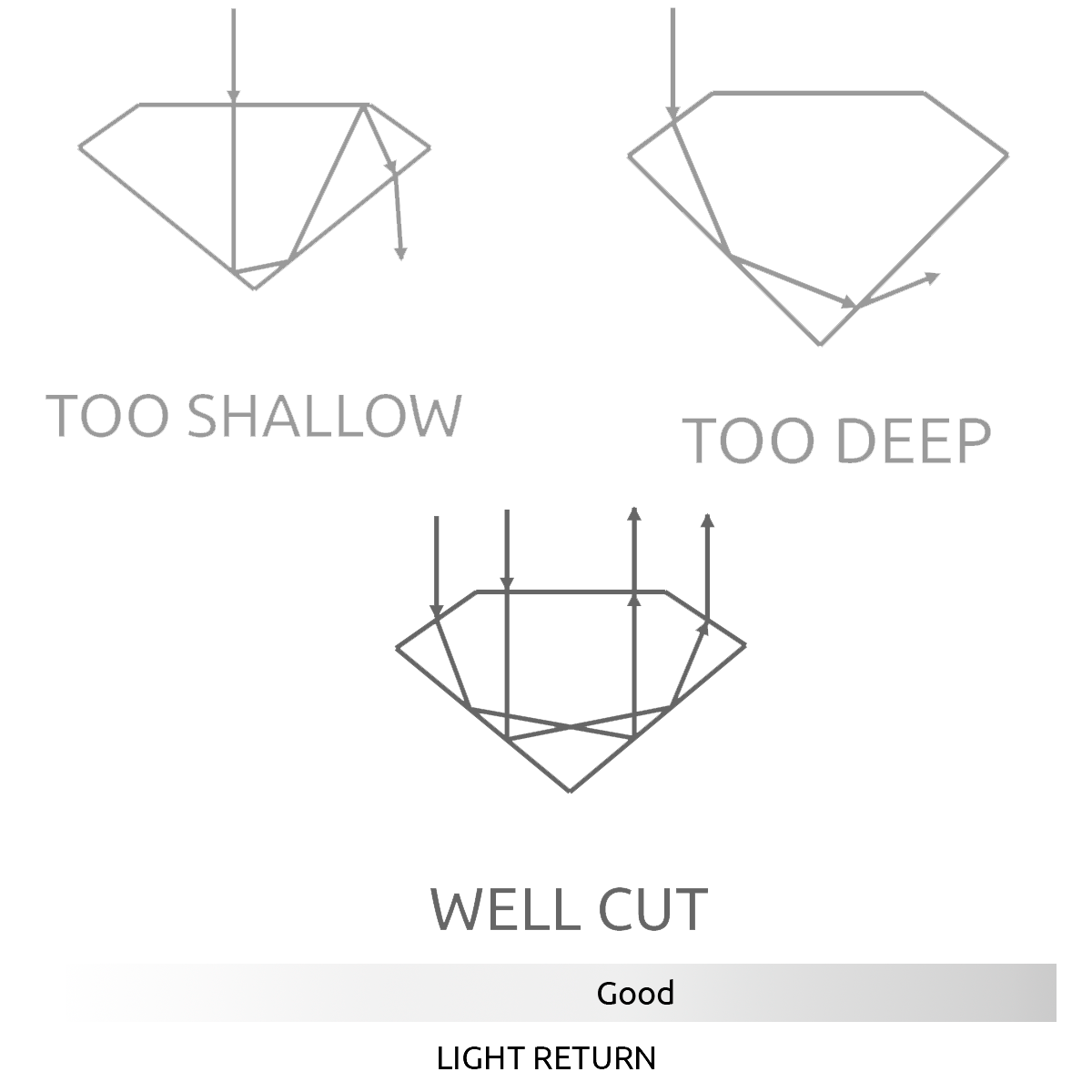
Diamonds are renowned for their ability to transmit light and sparkle so intensely. We often think of a diamond's cut as shape (round, emerald, pear), but a diamond's cut grade is really about how well a diamond's facets interact with light.
The quality of cut is crucial to the diamond's final beauty and value. And of all the 4Cs, it is the most complex and technically difficult to analyze.